Google Scholar / Publish or perish
Google Scholar (GS) citations / author profile
Google Scholar citations provide a simple way to keep track of citations to author’s publications. Researchers can create a Google Scholar profile (gmail account) and add there all their publications found through the Google Scholar search. My citations link (“omat lainaukset” in Finnish) shows the list of publications, the number of times the publications have been cited, h-index and i10-index (the number of publications with over 10 citations). Author profile example.
The profile can be public or private. When searching GS by an author, the public profile will be at the top of the results.
Compared to Web of Science and Scopus, Google Scholar covers more books, book chapters, theses, conference proceedings, technical reports and other publication types. It also has a wider range of journals and publications in other languages than English. Even so, the coverage of Google Scholar is uncontrolled, and there is no list of all publications included. The data are obtained from academic publishers, professional societies, online repositories, universities and other websites. Google Scholar does not separate non-scientific material (such as seminar presentations, working papers or master’s and bachelor’s theses) from scientific, scholarly literature. There is neither information available about the time span.
Google Scholar is also easy to manipulate. Read: The Google Scholar Experiment: how to index false papers and manipulate bibliometric indicators / Emilio Delgado López-Cózar, Nicolás Robinson-García. (Also part of the assignment of the course module.)
Google Scholar generally provides a higher citation count than Web of Science or Scopus, especially in the fields of social sciences, arts and humanities. The natural and health sciences are better covered in those databases. Google Scholar as a source for citation information differs significantly from scientific citation databases. Google Scholar citations are not always from scholarly journals or books.
How to set up your Google Scholar profile (Slideshare)
Publish or Perish (PoP)
Publish or Perish is a free software program which uses Google Scholar citation data to calculate the impact metrics including h-index and others. The main focus is on author’s impact, but it is also possible to examine the impact of a journal or analyse an individual article.
The program is developed by Dr. Anne-Wil Harzing of the University of Melbourne. It must be downloaded from Harzing’s web pages (no need for administrator rights).
Because it uses Google Scholar data, the limitations are the same. It is good to keep in mind the undefined contents of Google Scholar and be critical about the quality and reliability of citation information retrieved. Many citations come from non-scholarly publications. Also self-citations are included. The output of Publish or Perish should not be compared with the output of Web of Science or Scopus. GS as a source for scientific citation information is inaccurate and undefined. Instead GS citation data tells more about the societal impact of publications.
How to find author’s citation data using Publish or Perish:
Publish or Perish mines all Google Scholar data and will present data on any authors – not only those with a public Google Scholar profile.
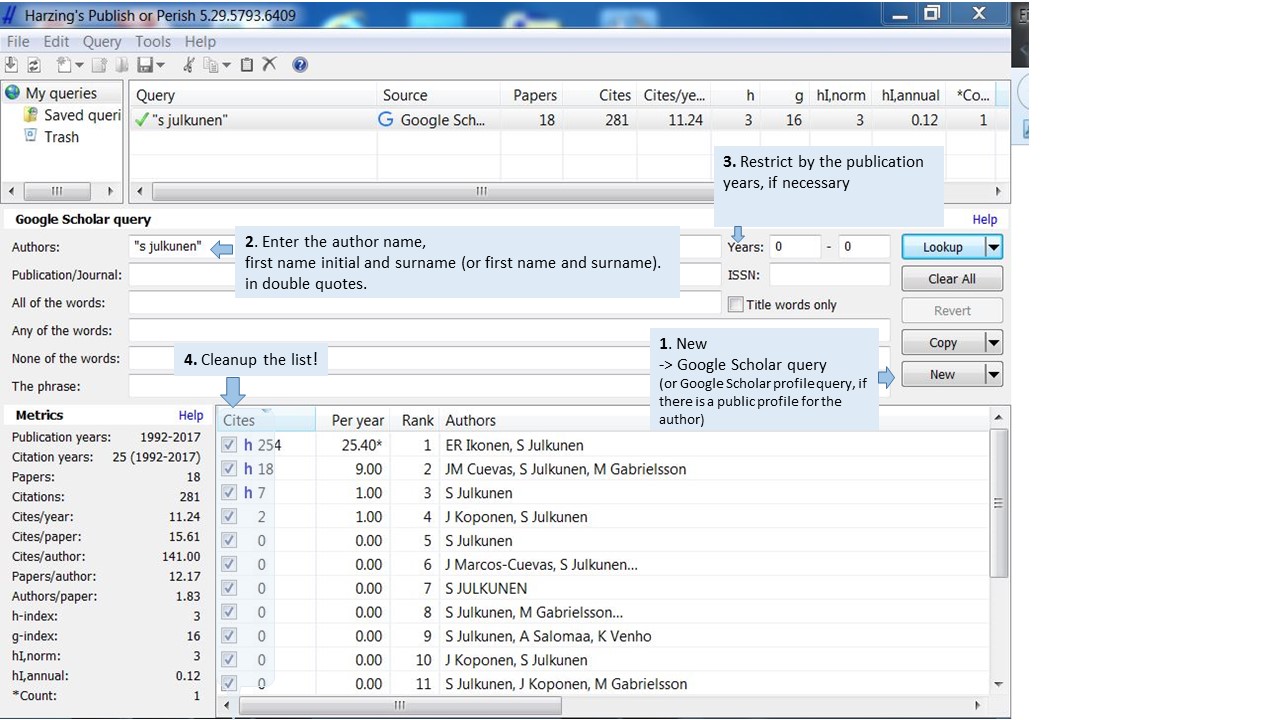
Cleaning up the results list:
It is possible that there are publications by another author with the same name or non-scholarly publications which you may not wish to include. Uncheck the boxes next to those records which you don’t want to be calculated to the results.
Often there are also duplicate entries to the same publication. Merge the duplicates by dragging one record on top of the other. Be careful to choose the most accurate one as the main reference.
The results are displayed in order of the citation count. You can change the order by clicking any of the column headings. If you have a long list of publications, it is useful to sort the results by title or year.
Behind the copy button you can export your list to Excel etc.
What if you have a very common author name? How to separate the works from those of “confuser” authors? Often it is good to have your publication list on hands. Sometimes the only way is to search for publications one by one and export those to excel (copy button on PoP main page). Maybe it would be good to create a profile of your own.
Further information:
Finnish national guide to publication metrics: Data sources: Google Scholar.
Finnish national guide to publication metrics: Analysis tools: Publish or Perish.
How to calculate researcher’s h-index with Publish of Perish (version 5) / University of Turku
– Please, scroll down to see the instructions.
Publish of Perish 6 manual / Harzing.com
– Related topics also
Impact of social sciences blog / London School of Economics and Political Science (LSE)
– Good blog for following the discussion especially for the researcher in the fields of social sciences.
(3/2023 JN)